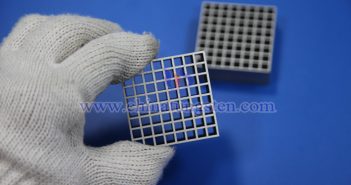
The application of tungsten alloy collimators in the medical field primarily focuses on diagnostic imaging and radiotherapy, owing to their high density, excellent radiation attenuation performance, heat resistance, and mechanical strength, making them essential components in medical equipment. Compared to traditional lead materials, tungsten alloy is more environmentally friendly, offers higher shielding efficiency, and enables thinner, lighter designs, making it ideal for space-constrained devices. 1. Diagnostic Imaging Field Tungsten alloy collimators are widely used in nuclear medicine imaging equipment, such…









