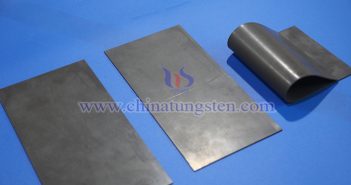
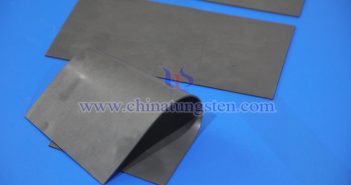
Tungsten is widely used in a variety of fields due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and high density. Tungsten’s uses include: Cemented carbide: Used in the manufacture of cutting tools, drills, molds, milling cutters, and wear-resistant parts such as cemented carbide inserts; cutting tools and molds, including turning tools, reamers, wire drawing dies, extrusion dies, and stamping dies, are widely used in metalworking, precision casting, and plastic molding. Aerospace components: Used in the manufacture…